SocialBook User Guide
SocialBook is a desktop app designed for social workers in Singapore, optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, SocialBook can get your contact management tasks done faster than traditional GUI apps. It helps you manage your beneficiaries by storing contact information, important remarks and information on the last time you visited them.
Quick start
Ensure you have Java
17or above installed in your Computer.Download the latest
.jarfile from here.Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your SocialBook.
Open a command terminal,
cdinto the folder you put the jar file in, and use thejava -jar socialbook.jarcommand to run the application.
A GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:list: Lists all contacts.view 2: Toggles the view on the 2nd contact shown in the current list with more/less information.add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 d/06-01-2024: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the SocialBook.delete 3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list.clear: Deletes all contacts.exit: Exits the app.
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Contact field requirements
Name
- Names are compulsory for all contacts, and are denoted with the
n/prefix. - Names can contain any characters at all, including spaces, hyphens, and other special characters.
- Names will be stored in their case-sensitive form, but capitalisation will be ignored when checking for duplicate names.
- Eg. Adding a contact as "john Doe" will save them as such, but trying to add a "John Doe" with the same phone number will be marked as a duplicate person and rejected.
- Also, names are checked in full, meaning that 'john doe' is not the same as 'john doe'
- To avoid unexpected behaviour with this, it is recommended that users save contacts with consistent capitalisation rules.
Phone
- Phones are compulsory for all contacts, and are denoted with the
p/prefix. - Phone numbers can only contain 8 numbers, and must begin with a 6, 8, or 9.
- Spaces in the middle of a phone number are accepted (eg. 9123 4523), as are phone numbers without spaces (eg. 91234523).
- Spaces in unusual locations will render the phone number invalid (eg. 912 34523).
Address
- Addresses are optional for contacts, and are denoted by the
a/prefix. - Addresses can contain any characters, including spaces, commas, hyphens, etc.
- To indicate no address for a contact, you can
adda contact without thea/prefix, or with aa/followed by whitespace.
- Emails are optional for contacts, and are denoted by the
e/prefix. - Email addresses are confined to the limits of the traditional email format:
localPart@domainName. This includes a few restrictions:- The
localPartcomponent of the email can only contain alphanumeric characters and the following 4 special characters:+,-,.,_. But take note that it cannot start or end with these special characters. - The
domainNamecomponent of the email will consist of one or more domain labels, separated by periods (.). - Every domain label can only contain alphanumeric characters, or hyphens (
-). They must also start and end with alphanumeric characters, so no starting or ending email addresses with hyphens! - The last domain label in the
domainNamemust be at least 2 characters long. - The
localPartanddomainNamecomponents of the email must be separated by a@.
- The
- To indicate no email for a contact, you can
adda contact without thee/prefix, or with ae/followed by whitespace.
Date of Last Visit
- Dates of last visit are optional for contacts, and are denoted by the
d/prefix. - Dates of last visit are confined to the
dd-MM-yyyyformat and range of dates follows the ISO-8601 calendar system. - The date provided must be valid, i.e., either today's date or any date before today. This prevents accidental entering of future dates.
- To indicate no date of last visit for a contact, you can
adda contact without thed/prefix, or with ad/followed by whitespace.
Emergency Contact
- Emergency contacts are optional fields, and are denoted by the
ec/prefix. - Emergency contacts are subject to the same formatting requirements as
Phone. - To indicate no emergency contact for a person, you can
adda contact without theec/prefix, or with aec/followed by whitespace.
Tags
- Tags are optional for contacts, and are denoted by the
t/prefix. - More than one tag can be added to a contact.
- Tags can contain any characters, but they should not begin with whitespace.
- You can include hyphens and spaces as necessary between words for tags that are multiple words long!
- To indicate no tags for a contact, you can
adda contact without anyt/prefixes.- Take note that
adding a contact with at/prefix followed by whitespace is not supported. Omit thet/tag for contacts without tags.
- Take note that
- Take note that tags are case sensitive i.e
financialandFINANCIALwould not be considered as duplicates.
Remarks
- Remarks are optional for contacts, and are denoted by the
r/prefix. - It is recommended that long-form notes about a particular contact should be saved in remarks.
- Remarks can contain any characters, as they allow long-form writing with multiple sentences.
- IMPORTANT: Only one
r/prefix can be used when adding remarks.- Adding another
r/prefix will cause the first part of ther/prefix to be lost. - If needed to add the prefix
r/to remark, enclose the prefix with " ". e.g.remark 1 r/ use "r/" to add remark
- Adding another
Take note: contacts will always be created without remarks. To write a remark about a contact, you can do this with the remark command, or with the edit command by specifying an r/ prefix.
Features
Notes about the command format:
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe.Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe.
e.gn/NAME [a/ADDRESS]can be used asn/Jane Smith a/123 Hollywood Street 55or asn/Jane Smith.Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used as(i.e. 0 times),t/friend,t/friend t/familyetc.Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable.Extraneous parameters will result in an error for the
listandviewcommands. Other commands likehelp,exit, andclearwill ignore any additional parameters and execute as intended. e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123,exit pleaseorclear 5, it will be interpreted as help, exit or clear respectively. However, if the command specifieslist somethingorview 2 3, it will throw an error.If you are using a PDF version of this document, be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines as space characters surrounding line-breaks may be omitted when copied over to the application.
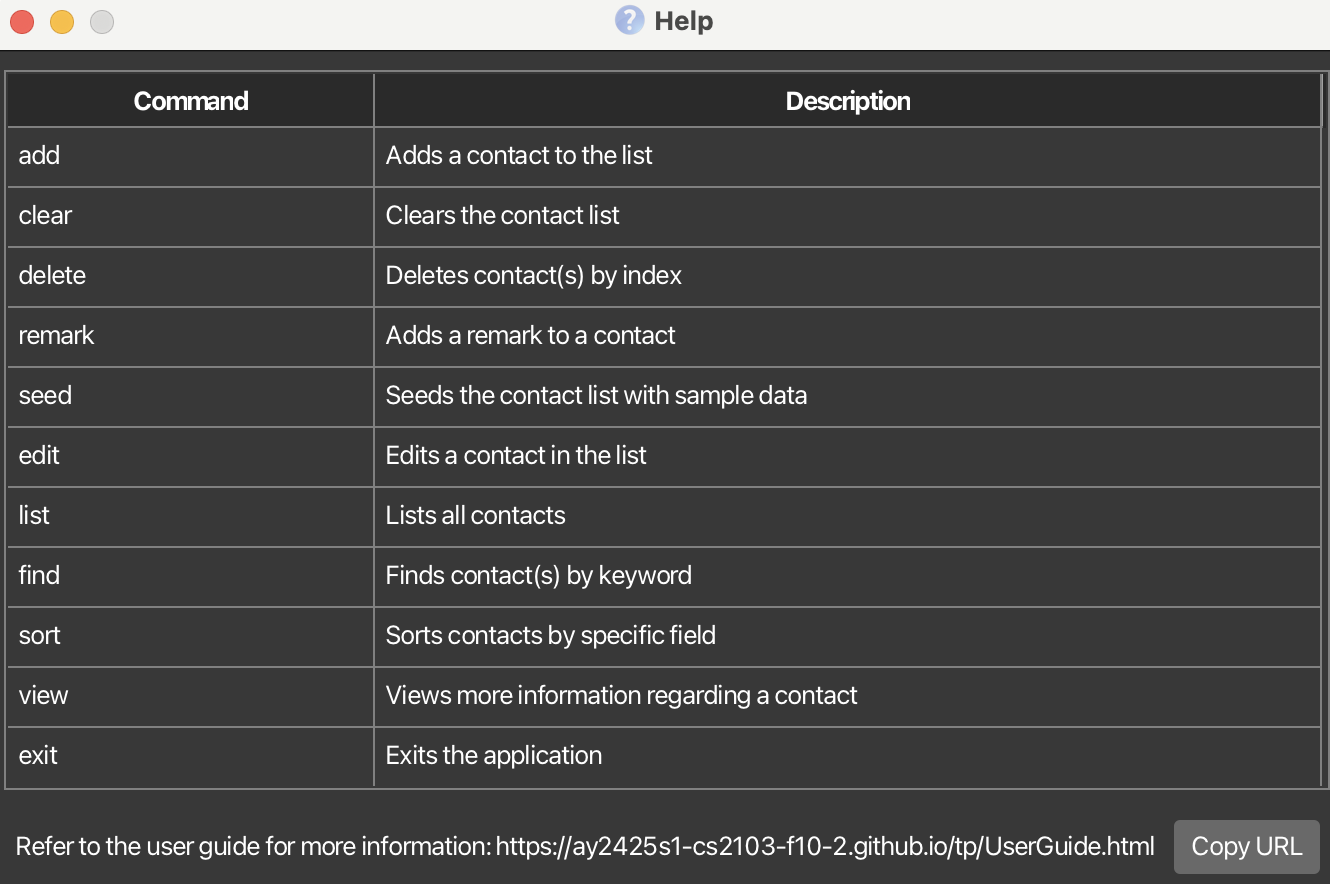
Viewing help : help
Shows a table of commands with their respective descriptions and a link to the user guide.
Format: help
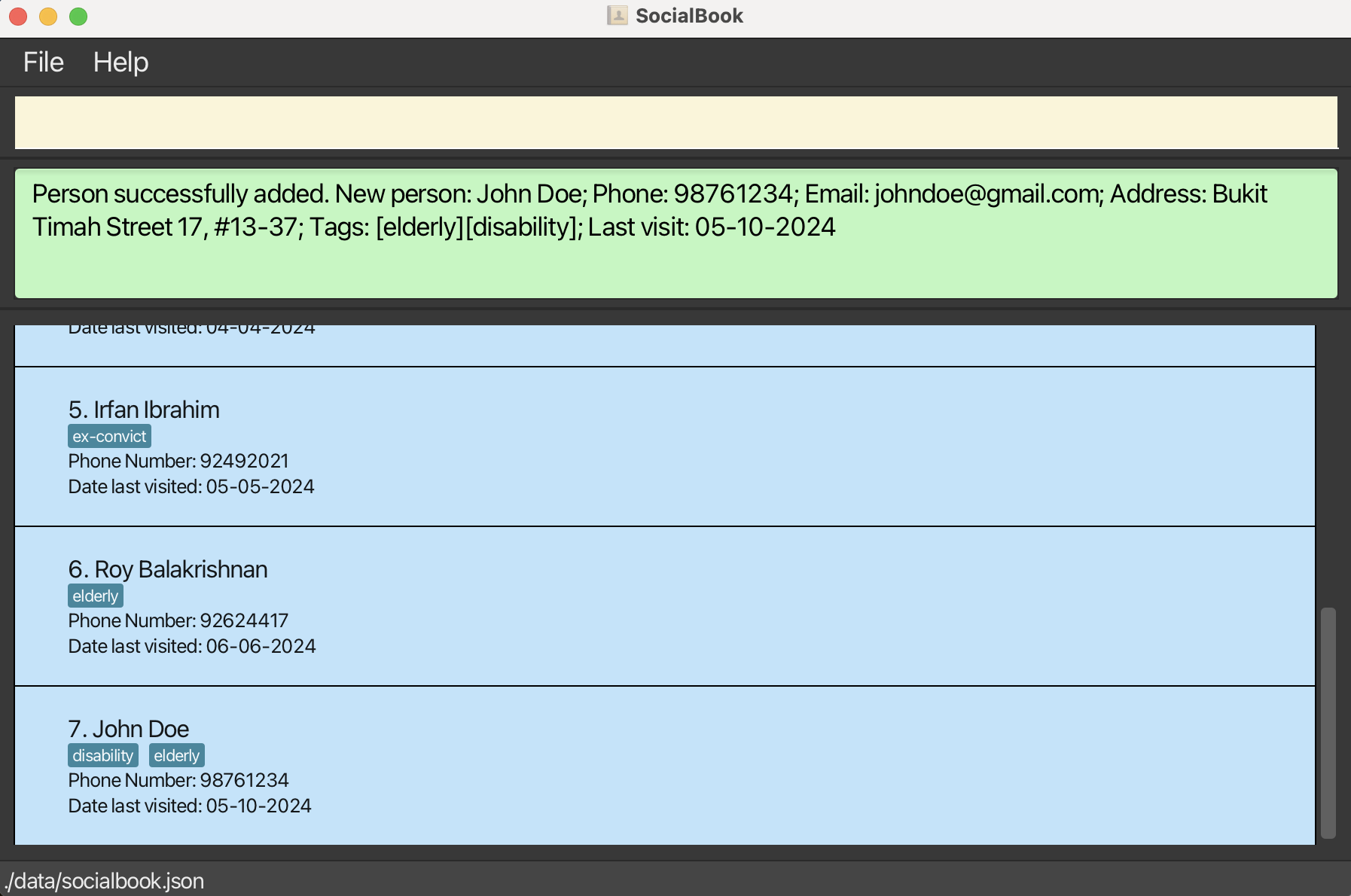
Adding a person: add
Adds a person to the address book with the provided information.
Format: add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]… [d/DATE_OF_LAST_VISIT] [ec/EMERGENCY_CONTACT]
- The only required fields for a person are a name and a phone number, so you can create a contact with just those 2 fields. Providing an email, address, date of last visit, emergency contact, or tags is optional.
- This
addcommand allows users to fill in all information fields about a person, except for the "remarks" field.- The "remarks" field is intended for long-form information about a person, so it is recommended that the addition of remarks be done with the
remarkcommand oreditcommand (which are explained below). - More information about the fields within a contact is located here.
- The "remarks" field is intended for long-form information about a person, so it is recommended that the addition of remarks be done with the
Tip: A person can have any number of tags (including 0).
Examples:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 d/02-01-2024add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/62345678 t/criminal d/28-03-2024add p/92345678 n/Jane Smith d/01-01-2024 ec/98765432add p/92345678 n/Sam Smith
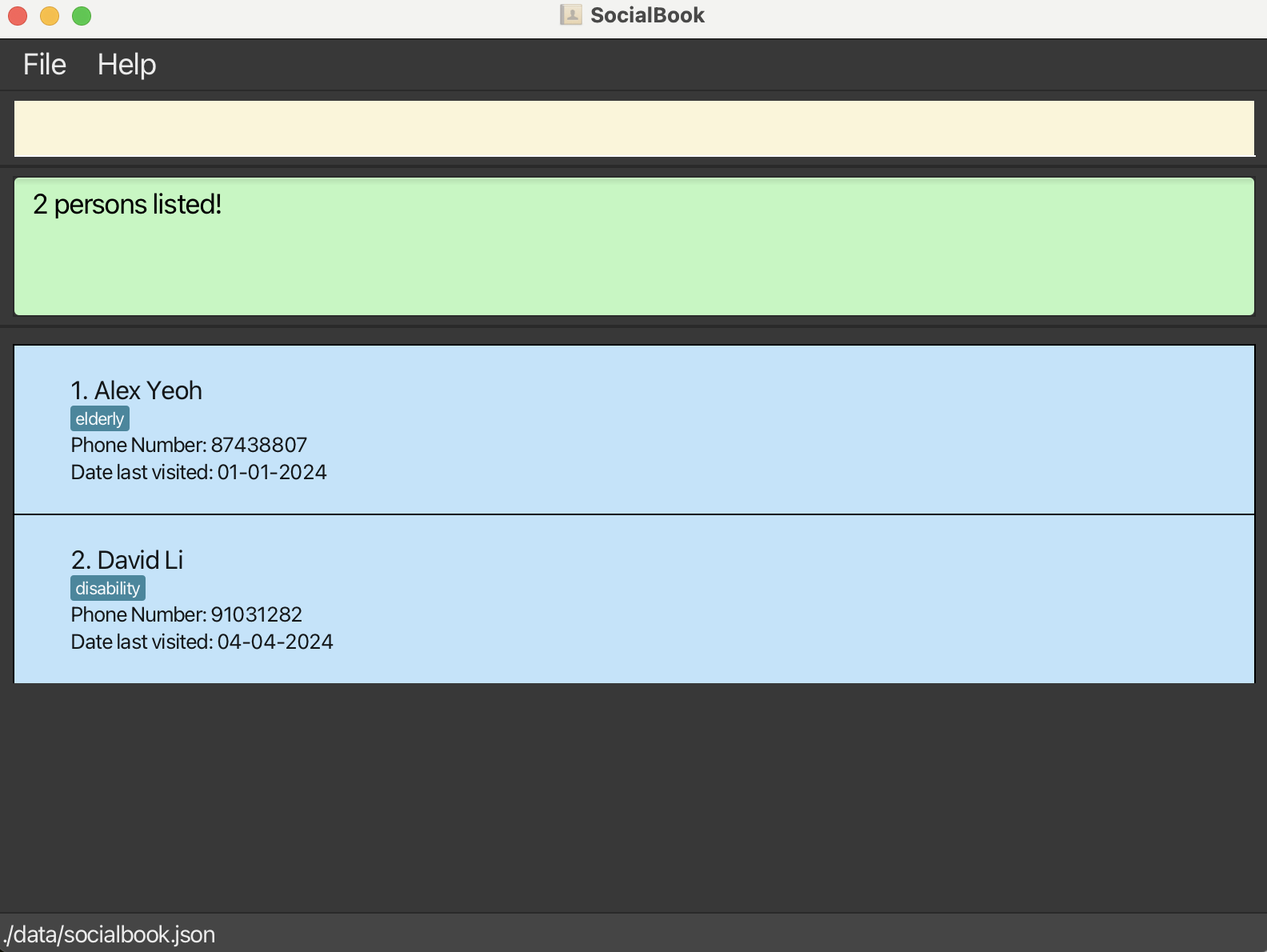
Listing all persons : list
Shows a list of all persons in the address book.
Format: list
Editing a person : edit
Edits an existing person in the address book.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]… [d/DATE_OF_LAST_VISIT] [ec/EMERGENCY_CONTACT] [r/REMARK]
- Edits the person at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the person will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the person’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it. - For optional fields (email, emergency contact, address, date of last visit, remark) you can delete them by entering the prefix without specifying any value after.
Examples:
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/ e/Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crower, clears all existing tags and deletes the stored email.
Locating specific persons: find
Finds contacts whose names or/and phone numbers or/and address or/and tags contain any of the given field keywords.
Format: find [n/NAMEKEYWORDS] [p/PHONEKEYWORDS] [a/ADDRESSKEYWORDS] [t/TAGKEYWORDS]
NOTE: At least one field MUST be provided
e.g. find n/Hans or find p/82345678 or find a/wall street will work
e.g. find Hans or find wall street or find will fail
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
hanswill matchHansorwall Streetwill matchWall Street - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Partial words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill matchHans - Contacts matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang - If more than one fields are specified, contacts will be matched by multiple fields (i.e.
ANDsearch). - For multiple address or tag keywords, they are separated by "_". e.g
find t/friends_colleague_owes moneyorfind a/wall street_michigan - For multiple name or phone keywords, they are separated by " ". e.g
find n/andy ben carlorfind p/98233211 81212899
Take Note: using an edit command on a contact after a find operation may remove them from the displayed list, if the contact is edited to no longer match the find requirements. Use the list command to return to the view of all contacts, or find them again with new parameters.
Examples:
find n/JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doefind n/alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li
find p/87438807 91031282returnsAlex Yeoh,David Lifind a/serangoonreturnsDavid Lifind n/alex p/87438807 a/geylangreturnsAlex Yeoh
Deleting a person : delete
Deletes the specified person or persons from the address book.
Format: delete INDEX delete INDEX INDEX ...
- Deletes the person or persons at the specified
INDEXorINDEX INDEX .... - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd person in the address book.find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.listfollowed bydelete 1 2deletes the 1st and 2nd person in the address book.
Adding remarks to person : remark
Add remarks to an existing person in the address book.
Format: remark INDEX r/REMARK
- Adds remarks to the person at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
remark 1 r/Financial IssuesAdds the remark of the 1st person to beFinancial Issues.remark 1 r/Clears remarks (if any) of the 1st person.
Sorting the person list : sort
Sorts the list of persons being viewed by name (prefix: n) or date of last visit (prefix: d) in ascending or descending order.
Format: sort PARAMETER_PREFIX/ORDER
- Sorts the contacts according to the parameter, in the specified order.
- By default, if
ORDERis omitted, contacts will be sorted in ascending order based on thePARAMETER. - An ascending order can be specified by replacing
ORDERwithascendingor its short formasc. - A descending order can be specified by replacing
ORDERwithdescendingor its short formdesc. - Ascending name order will generally be special characters and numbers followed by letters (case-insensitive).
- Persons without date of last visit will always appear at the end when sorting by date of last visit.
Examples:
sort n/sorts by name in ascending order.sort d/,sort d/asc,sort d/ascendingare all equivalent, and they sort by date of last visit in ascending order.sort d/descsorts by date of last visit in descending order.
Viewing a person : view
Toggles the contact card on the specified person, switching between more and less information.
The default view for all contact cards will display less information to avoid visually overwhelming users, but users may decide to toggle the view for all information on one or more persons.
Format: view INDEX
- This command permits the user to
viewmore information about a contact. Using theviewcommand on a contact that's already expanded will collapse it back to its default view. - Viewing is done by index, and not the person's name or any other field. Attempting to
viewby name, address, or any other fields will result in an error. - View is intended for short term ad-hoc usage, and the view states of contact cards will not persist between sessions.
Examples:
view 2will expand the contact card for the second person in the contact list.
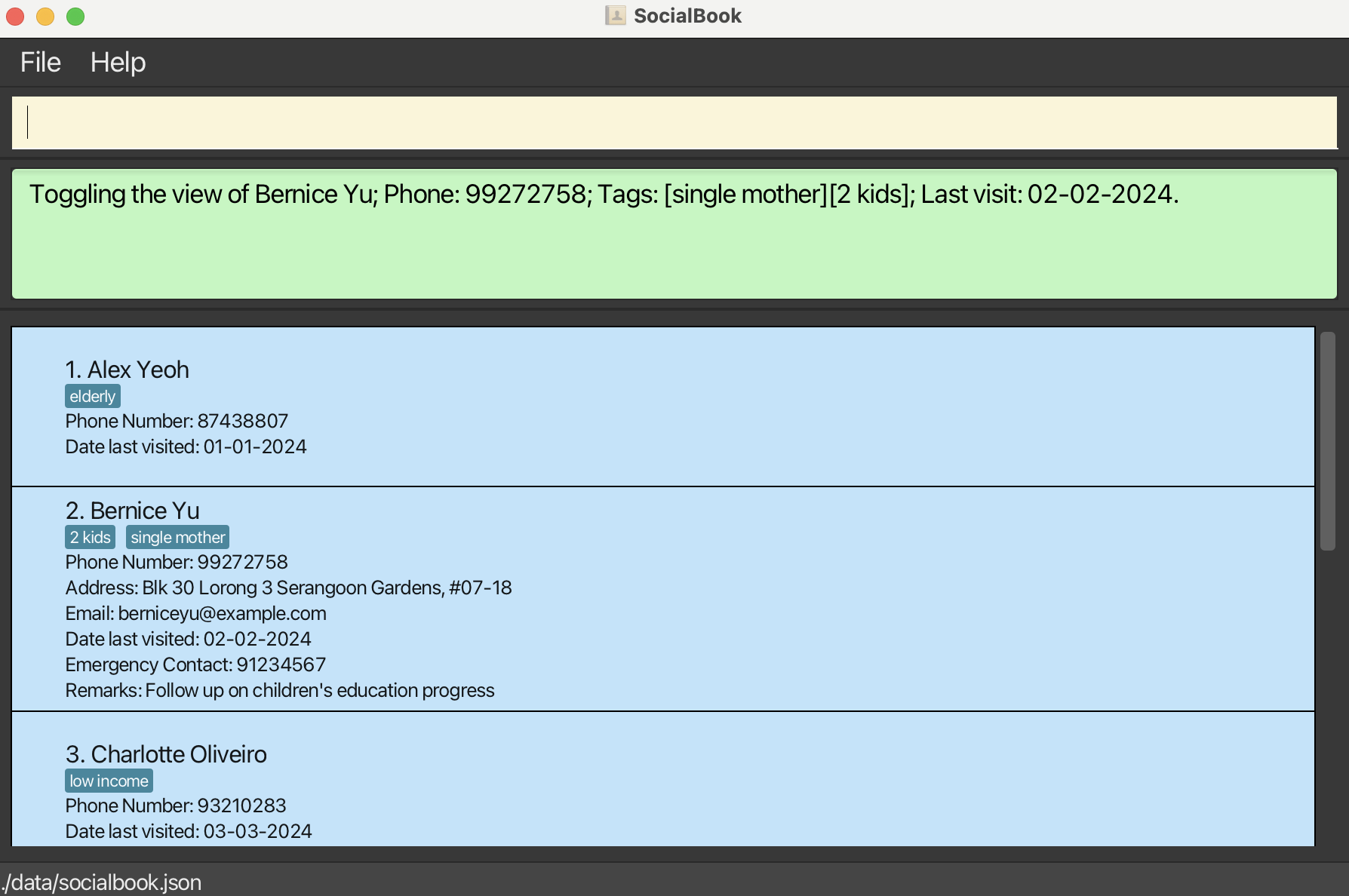
- Using
view 2again will collapse the contact card back down to its default view.
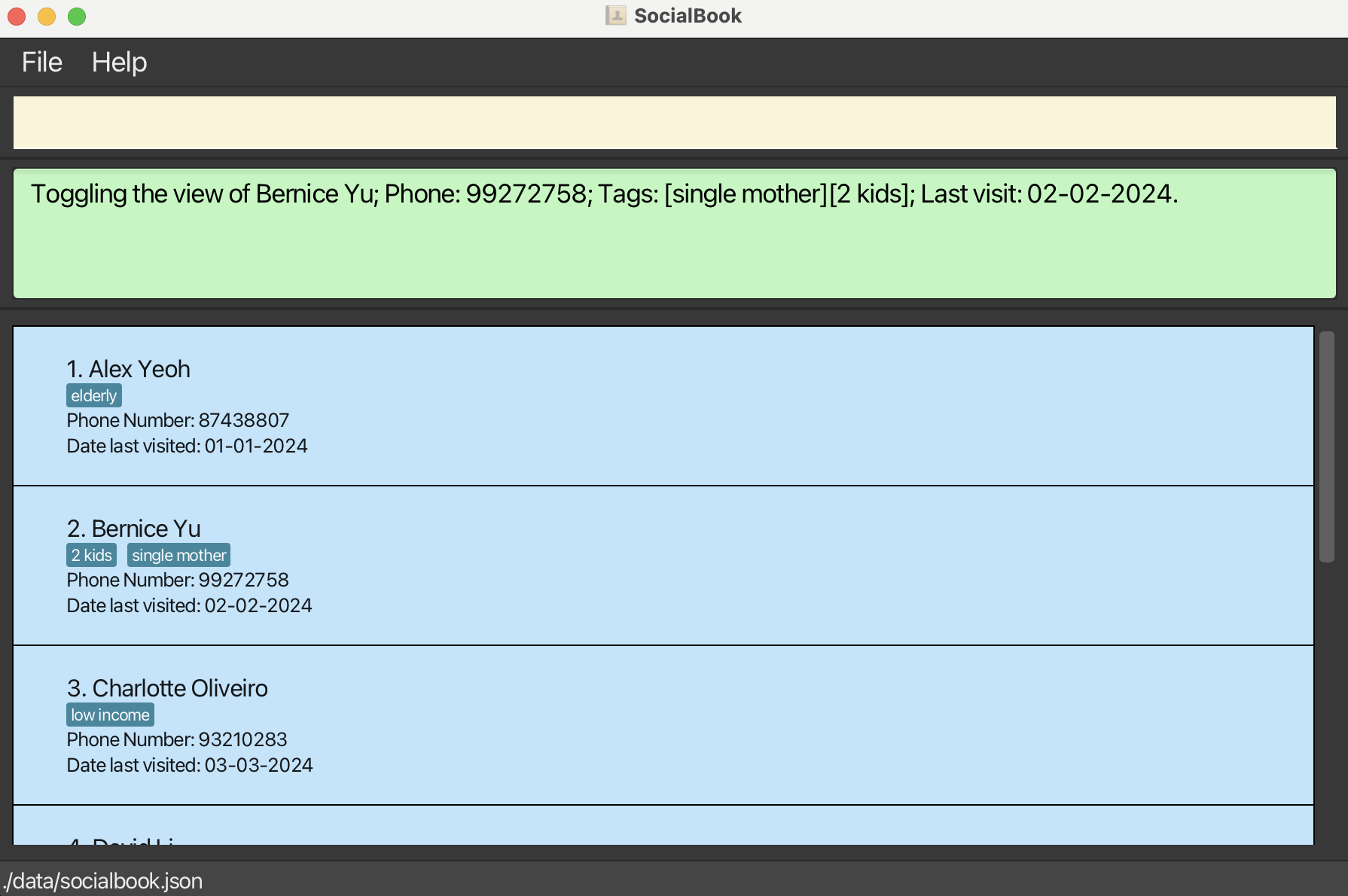
Take Note: Viewing is executed based on the currently displayed list.
Executing any commands that alter the displayed list (such as delete, sort, or find) may change the person being viewed.
For this reason, it is recommended to execute view commands after the displayed list has been modified as intended.
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
Populating with dummy data : seed
Adds dummy data to the address book.
Format: seed
NOTE: There are 6 contacts in the dummy data. seed works in a way that would be similar to if the user were to iteratively issue add command on the 6 person. This means that,
seedwill add them to the contact list if they are not presently inside.seeddoes not clear or reset the list.- If your existing contact list has a person with the same name and phone number, it will not be overwritten.
Note: Seed command does not inform you if a duplicate person was skipped, it will only state that it has "seeded sample data" regardless of outcome.
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Saving the data
SocialBook data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
SocialBook data are saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/socialbook.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Caution:
If a person's data values are changed to an invalid format, Socialbook will discard that particular person's data while keeping the rest. However, if your changes to the data file makes the file format invalid, SocialBook will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run only if user exits SocialBook with the exit command. Hence, it is recommended to take a backup of the file before editing it.
Furthermore, certain edits can cause the SocialBook to behave in unexpected ways (e.g., if a value entered is outside the acceptable range). Therefore, edit the data file only if you are confident that you can update it correctly.
FAQ
Q1: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
- Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous SocialBook home folder.
Q2: Why can't I include a remark when using the add command to add a person to the address list?
- The "remarks" field is meant for long form notes about a person. This is likely to be quite cumbersome to enter at the same time that a person is being added for the first time.
- Users are recommended to first
addthe person to the address list, and then subsequently use theeditorremarkcommands to write remarks about a contact.
Q3: How does SocialBook determine a duplicate contact?
- First of all, we consider a duplicate as a person having both identical name (case-insensitive) and phone number.
- To understand this, we look at the following cases and explain why they should not be considered a duplicate.
- Persons with the same name but different phone numbers are common, and are clearly not duplicates.
- Persons with different names but the same phone number can exist in the field of social work, and should not be considered duplicates. If multiple beneficiaries live in the same shared rental flat, they may share the same phone number (on a landline). For the social worker to remember each person's contact separately, it makes sense to not mark these contacts as duplicates so that remarks and tags can be added to each person's contact.
- Persons with different names and different phone numbers are definitely different people, and are thus not duplicates.
Known issues
- When using multiple screens, if you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the
preferences.jsonfile created by the application before running the application again. - If you minimize the Help Window and then run the
helpcommand (or use theHelpmenu, or the keyboard shortcutF1) again, the original Help Window will remain minimized, and no new Help Window will appear. The remedy is to manually restore the minimized Help Window. - When editing contacts with the
editorremarkcommand, the result display panel will not show the updated or changed information. Use theviewcommand on the person of interest to view the updated details. - Some of the commands that edit contacts (such as
addandedit) may have difficulty parsing input if some input fields match the prefixes for contact fields (such asn/,p/,a/,e/,d/,ec/,t/, andr/). This is due to the way that parsing is handled: any text matching special prefixes will be identified as such. To work around this, please prepend a_, or any other accepted special character, in front of any input fields that contain a special prefix. - Entering an invalid emergency contact will produce the same error message as an invalid phone number. When receiving an error message about phone numbers, check both the
ec/andp/field, if both are present. - Tags with the same name but with different cases are considered two different tags i.e
freeandFREEare not considered duplicates.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add | add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]… [d/DATE_OF_LAST_VISIT] [ec/EMERGENCY_CONTACT] e.g., add n/James Ho p/82224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague d/23-07-2024 |
| Clear | clear |
| Delete | delete INDEXe.g., delete 3 |
| Edit | edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]… [d/DATE_OF_LAST_VISIT] [ec/EMERGENCY_CONTACT] [r/REMARK] e.g., edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com |
| Find | find [n/NAMEKEYWORD] [p/PHONEKEYWORD] [a/ADDRESSKEYWORD] [t/TAGKEYWORD]e.g., find n/James Jake a/clementi street_woodlands |
| List | list |
| View | view INDEXe.g., view 1 |
| Help | help |
| Seed | seed |
| Sort | sort PARAMETER_PREFIX/ORDER e.g., sort n/ascending |
| Remark | remark INDEX r/REMARK e.g., remark 1 r/some remark about contact |